Leveraging NHBS Data at the Local Level
NHBS data are used to provide a behavioral context for trends seen in national HIV surveillance data. They also describe populations at increased risk for HIV infection and thus provide an indication of the leading edge of the epidemic. Through systematic surveillance in groups at high risk for HIV infection, NHBS is critical for monitoring the impact of the National HIV/AIDS Strategy, which focuses on decreasing HIV incidence, improving linkage to care, and reducing disparities.
In addition to informing HIV behavioral surveillance at the national level, NHBS can be leveraged to inform local trends.
As part of the National HIV Behavioral Surveillance (NHBS) system, the Public Health Institute at Denver Health has provided testing for the hepatitis C virus during several cycles. Sharing needles, syringes, and other equipment used to prepare and inject drugs can transmit hepatitis C and other blood borne infections, such as HIV and hepatitis B.
Testing using blood from a finger stick with the OraQuick® HCV Rapid Antibody test was offered to NHBS participants during data collection in 2014, 2015, and 2016.
HCV antibody status, awareness and treatment history among NHBS participants:
| MSM (2014) | PWID (2015) | HET (2016) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HCV antibody + | 2% (11/455) | 60% (344/577) | 9% (44/471) |
| Aware of infection | 91% (10/11) | 79% (271/344) | 86% (38/44) |
| Ever taken HCV medication | 50% (5/10) | 11% (29/271) | 45% (17/38) |
In 2018, HCV testing was offered during the PWID cycle. Of the 545 participants who consented to HCV testing, 349 (64%) were antibody positive and 283 (52%) self-reported being positive.
HCV status by years since first injection among persons who inject drugs, 2018:

As part of the National HIV Behavioral Surveillance (NHBS) system, persons who inject drugs (PWID) are asked about the drug most frequently injected in the past 12 months. The shift from heroin to methamphetamine is clear over the cycles. In the 2024 cycle, 51% of PWID reported injecting fentanyl in the past 12 months.
Changes in Most Frequently Injected Drug Over Time Among Persons Who Inject Drugs
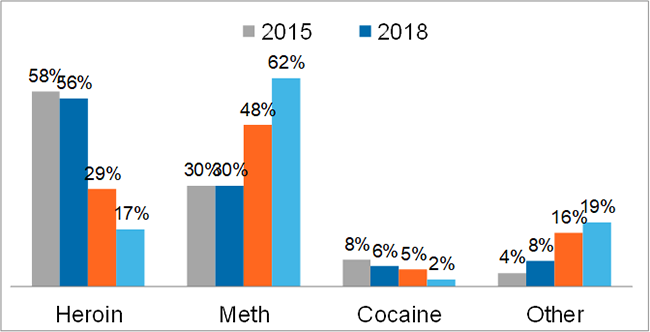
NOTE: In 2018, “other” mostly reported as goofballs (heroin and meth). In 2022, 25% of “other” reported as fentanyl. In 2024, 40% of “other” reported as fentanyl.
In 2022 and 2024, participants were asked if they changed the way they used drugs because of the presence of fentanyl. More participants reported to changing mostly smoking or snorting in 2022.
Changes in Drug Use Patterns in the Past 12 Months due to Fentanyl, 2022 vs. 2024

More detailed information about the 2024 NHBS-PWID cycle can be found in the report linked below.


